■ 다익스트라(Dijkstra) 알고리즘
다익스트라 알고리즘은 가중치 있는 그래프에서 시작 노드부터 다른 노드들까지의 최단 경로를 찾는다.
- 시작 노드로부터 모든 노드에 대한 최단 경로를 계산한다.
- 가중치는 음수일 수 없다.
- 다익스트라는 그라디(Greedy) 알고리즘이며, 동적 배열 갱신 과정에서 다이내믹 프로그래밍의 성격도 일부 포함된다
그라디 알고리즘과 다이나믹 프로그래밍에 대해 정리한 부분은 아래에서 참조할 수 있다.
▼ 그라디 알고리즘
2025.04.10 - [Unity,C#/알고리즘] - [C#, Algorithm] 그라디(탐욕, 욕심쟁이) 알고리즘
[C#, Algorithm] 그라디(탐욕, 욕심쟁이) 알고리즘
■ 그라디(Greedy) 알고리즘그라디(탐욕, 욕심쟁이) 알고리즘은 매 단계에서 “가장 좋아 보이는 선택”을 하는 알고리즘이다. 이 선택이 전체적으로도 최적일 거라는 가정 하에 작동한다.항상 최
hate-errorlog.tistory.com
▼ 다이나믹 프로그래밍
2025.04.10 - [Unity,C#/알고리즘] - [C#, Algorithm] Dynamic Programming(동적 계획법)
[C#, Algorithm] Dynamic Programming(동적 계획법)
■ Dynamic Programming(동적 계획법)큰 문제를 작은 문제로 나누고, 그 작은 문제의 결과를 저장하여 같은 계산을 반복하지 않도록 하는 알고리즘 기법이다.중복 부분 문제 (Overlapping Subproblems)동일한
hate-errorlog.tistory.com
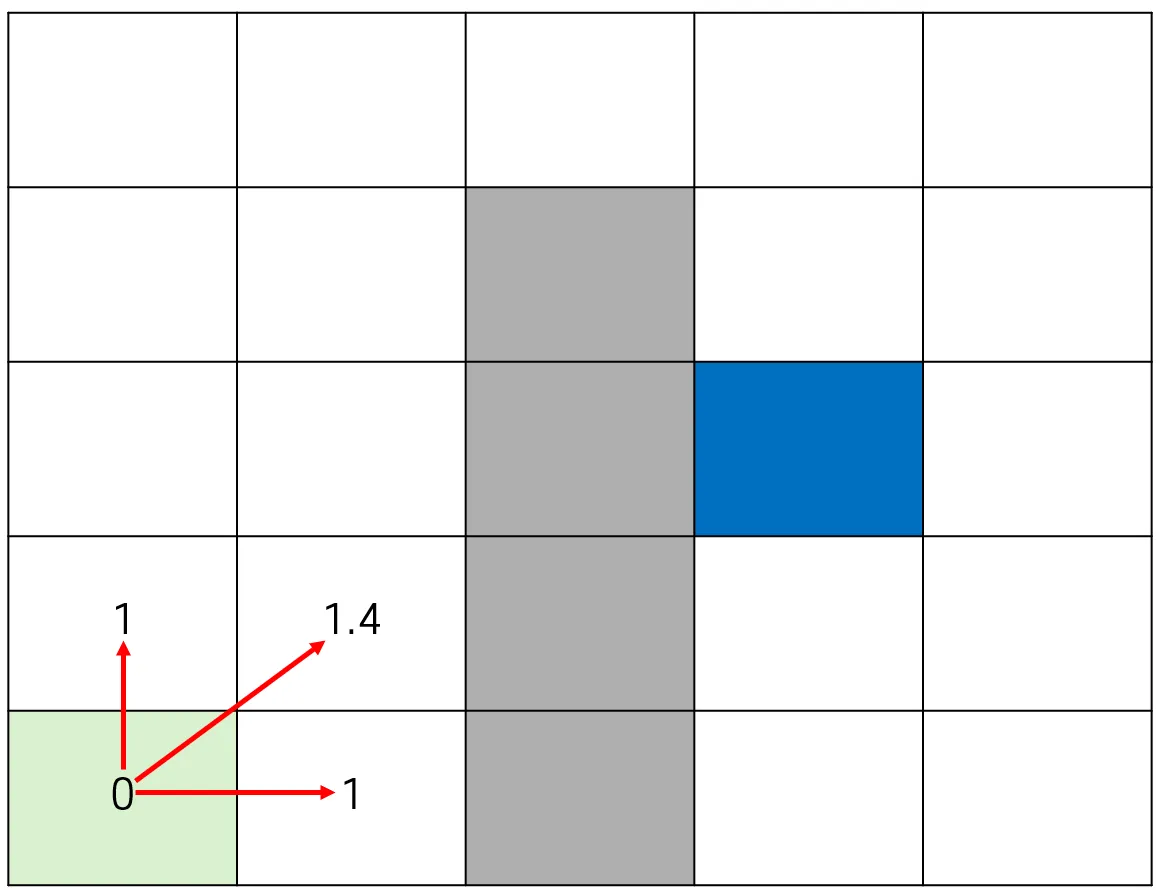
다익스트라는 시작 노드로부터 인접한 노드들까지의 비용을 우선 계산한 후, 그 중 가장 짧은 거리의 노드를 선택하여 탐색을 이어나간다.
- 현재 노드를 방문 처리한다.
- 인접한 노드들 중, 방문하지 않았거나 이동 가능한 노드(장애물이 아닌)로 가는 이동 비용을 저장한다.

거리가 계산된 노드 중, 가장 적은 비용을 가지고 있는 노드를 선택하여 인접 노드를 비교한다. 현재 노드까지 움직인 비용 + 인접노드로 이동할 때의 비용을 더해 비용을 갱신한다.
- 비용을 갱신할 때, 현재 노드(초록색)의 인접한 노드인 A와 B는 이미 이전 단계에서 거리가 계산된 상황일 수 있다.
- 이전에 계산된 A 또는 B로의 경로보다, “현재 노드를 거쳐가는 경로”가 더 짧을 경우에만 비용과 부모를 갱신한다.
이런 방식으로 도착 지점을 찾을 때까지, 모든 노드를 탐색하며 비용을 기록한다.
■ 다익스트라 구현(Unity, C#)
다익스트라는 BFS와 유사한 방식으로 탐색하지만, 크게 차이나는 점은 큐(Queue) 대신 우선순위 큐(Priority Queue)를 사용한다는 점이다.
2025.04.08 - [Unity,C#/자료구조] - [C#, Unity] 우선순위 큐(PriorityQueue)
[C#, Unity] 우선순위 큐(PriorityQueue)
■ 개요Queue와 같이 FIFO(먼저 들어온 요소가 먼저 나감)처럼 삽입은 순서대로 하지만, 꺼낼 때는 우선순위가 높은(낮은) 순서로 꺼내지게 된다.중복을 허용하며, 우선순위가 같다면 일반적으로
hate-errorlog.tistory.com
▶ 경로 복원
최단 경로를 찾기 위해서는 각 노드(타일)가 어느 노드로부터 탐색되었는지, 즉 부모 노드 정보를 저장해야 한다. 그래야 도착 지점에 도달했을 때, 거슬러 올라가며 시작 지점까지의 경로를 복원할 수 있다.
좌표는 2차원 배열 인덱스를 기준으로 (y, x) 형식으로 기록하며, 탐색 과정은 다음과 같다.
- 노드 A(1,1)는 Start노드로부터 탐색되었기 때문에, A노드에는 Start노드의 위치(2,1)를 기록한다.
- 노드 B(0,1)는 A노드로부터 탐색되었기 때문에, B노드에는 A노드의 위치를 기록한다.
- 도착 지점을 찾을 때까지 기록한 뒤, 도착 지점을 찾으면 거슬러 올라가 시작 위치까지의 경로를 저장한다.
1. Tile
먼저, 가중치를 표현하기 위해 TileMap에서 각 타일에 대한 정보를 저장하기 위한 클래스를 생성하였다.
public class Tile
{
public int Weight { get; private set; }
public Material Mat { get; private set; }
private readonly Color _originColor;
public Tile(GameObject obj, int weight)
{
Mat = obj.GetComponent<Renderer>().material;
_originColor = Mat.color;
Weight = weight;
}
public void ResetColor()
{
Mat.color = _originColor;
}
}
좌표 정보는 Tile을 저장하는 이차원 배열의 인덱스로 충분히 표현 가능하므로, Tile 클래스 내부에 따로 저장하지 않았다.
- Weight : 해당 타일로 이동할 때, 소모되는 비용을 의미한다.
2. 다익스트라
public List<(int, int)> Dijkstra_PathFinding(Tile[,] tile, (int, int) start,
(int, int) end)
{
var height = tile.GetLength(0);
var width = tile.GetLength(1);
var visited = new bool[height, width];
var distance = new float[height, width];
var parent = new (int, int)[height, width];
for (var i = 0; i < height; ++i)
{
for (var j = 0; j < width; ++j)
{
distance[i, j] = int.MaxValue;
}
}
var pq = new PriorityQueue<(int, int), float>();
pq.Enqueue(start, 0);
distance[start.Item1, start.Item2] = 0;
}
다익스트라 알고리즘을 구현하기 위해 필요한 변수들을 먼저 선언한다.
- visited[,] : 방문 정보를 기록할 이차원 배열.
- distance[,] : 비용을 저장할 이차원 배열.
- parent[,] : 부모 타일의 좌표를 저장할 이차원 배열.
- pq : 우선순위 큐. 데이터로는 Tile의 좌표(y, x)가 저장되고, 우선순위로는 해당 위치까지의 누적 비용을 저장한다.
거리를 기록하기 위해, distance의 모든 요소는 무한대(INF)로 설정하여, 이후 계산되는 비용이 이를 갱신하도록 만든다.
public List<(int, int)> Dijkstra_PathFinding(Tile[,] tile, (int, int) start,
(int, int) end)
{
//
// 생략
//
while (pq.Count > 0)
{
pq.TryDequeue(out var node, out var priority);
if(visited[node.Item1, node.Item2] == true) continue;
if (node == end) return PathUtils.FindShortPath(parent, start, end);
visited[node.Item1, node.Item2] = true;
var cnt = -1;
foreach (var dir in PathUtils.SearchDir)
{
cnt++;
var xPos = node.Item2 + dir.x;
var yPos = node.Item1 + dir.y;
if(xPos < 0 || xPos >= width || yPos < 0 || yPos >= height) continue;
if(visited[yPos, xPos] == true || tile[yPos, xPos].Weight == (int)EBiome.WALL) continue;
// 대각선 이동 가능 검사
if (cnt >= 4 && PathUtils.IsDiagonalBlocked(tile, node, (yPos, xPos)) == true)
{
continue;
}
var weight = (cnt >= 4) ? tile[yPos, xPos].Weight * 1.4f : tile[yPos, xPos].Weight;
var newDistance = weight + priority;
if (newDistance > distance[yPos, xPos])
{
continue;
}
pq.Enqueue((yPos, xPos), newDistance);
distance[yPos, xPos] = newDistance;
parent[yPos, xPos] = node;
}
}
우선순위 큐에서 누적 비용이 가장 낮은(= 우선순위가 높은) 노드를 꺼낸 후, 해당 노드를 방문 처리하고 탐색을 시작한다.
public static readonly Vector2Int[] SearchDir = new[]
{
new Vector2Int(0, -1), new Vector2Int(0, 1), // 상, 하
new Vector2Int(-1, 0), new Vector2Int(1, 0), // 좌, 우
new Vector2Int(-1, -1), new Vector2Int(-1, 1), // 좌상, 좌하
new Vector2Int(1, -1), new Vector2Int(1, 1) // 우상, 우하
};
- 이후 8방향으로 인접한 노드를 탐색한다. PathUtils.SearchDir은 Vector2Int 배열로 정의되어 있으며, 반복문을 통해 인접 노드를 간결하게 순회할 수 있도록 구성되어 있다.
var weight = (cnt >= 4) ? tile[yPos, xPos].Weight * 1.4f : tile[yPos, xPos].Weight;
var newDistance = weight + priority;
if (newDistance > distance[yPos, xPos])
{
continue;
}
pq.Enqueue((yPos, xPos), newDistance);
distance[yPos, xPos] = newDistance;
parent[yPos, xPos] = node;
이동 가능한 노드들을 골랐으면, 가장 중요한 부분이 다음 부분이다.
- cnt 값이 4 이상이면, 현재 탐색 중인 노드는 대각선 방향에 위치하므로, 기존 가중치에 1.4를 곱해 대각선 이동 비용을 반영한다.
- 계산된 비용이 기존 distance에 저장된 값보다 작을 경우, 해당 노드까지의 최소 비용과 부모 노드를 갱신한다.
■ 전체 코드 및 실행 결과
- 결과를 확인해보면, 색 타일(노랑 - 3, 갈색 - 5, 보라 - 8)을 피한 경로를 찾는다.
public List<(int, int)> Dijkstra_PathFinding(Tile[,] tile, (int, int) start, (int, int) end)
{
var height = tile.GetLength(0);
var width = tile.GetLength(1);
var visited = new bool[height, width];
var distance = new float[height, width];
var parent = new (int, int)[height, width];
for (var i = 0; i < height; ++i)
{
for (var j = 0; j < width; ++j)
{
distance[i, j] = int.MaxValue;
}
}
var pq = new PriorityQueue<(int, int), float>();
pq.Enqueue(start, 0);
distance[start.Item1, start.Item2] = 0;
while (pq.Count > 0)
{
pq.TryDequeue(out var node, out var priority);
PrefCheck.AddCheckTile(node);
if(visited[node.Item1, node.Item2] == true) continue;
if (node == end)
{
return PathUtils.FindShortPath(parent, start, end);
}
visited[node.Item1, node.Item2] = true;
var cnt = -1;
foreach (var dir in PathUtils.SearchDir)
{
cnt++;
var xPos = node.Item2 + dir.x;
var yPos = node.Item1 + dir.y;
if(xPos < 0 || xPos >= width || yPos < 0 || yPos >= height) continue;
if(visited[yPos, xPos] == true || tile[yPos, xPos].Weight == (int)EBiome.WALL) continue;
// 대각선 이동 가능 검사
if (cnt >= 4 && PathUtils.IsDiagonalBlocked(tile, node, (yPos, xPos)) == true)
{
continue;
}
var weight = (cnt >= 4) ? tile[yPos, xPos].Weight * 1.4f : tile[yPos, xPos].Weight;
var newDistance = weight + priority;
if (newDistance > distance[yPos, xPos])
{
continue;
}
pq.Enqueue((yPos, xPos), newDistance);
distance[yPos, xPos] = newDistance;
parent[yPos, xPos] = node;
}
}
return null;
}public static class PathUtils
{
public static readonly Vector2Int[] SearchDir = new[]
{
new Vector2Int(0, -1), new Vector2Int(0, 1),
new Vector2Int(-1, 0), new Vector2Int(1, 0),
new Vector2Int(-1, -1), new Vector2Int(-1, 1),
new Vector2Int(1, -1), new Vector2Int(1, 1)
};
public static List<(int, int)> FindShortPath((int, int)[,] parent, (int, int) start,
(int, int) end)
{
var result = new List<(int, int)>();
var current = end;
while (current != start)
{
result.Add(current);
current = parent[current.Item1, current.Item2];
}
result.Add(start);
result.Reverse();
return result;
}
public static bool IsDiagonalBlocked(Tile[,] tile, (int y, int x) curNode, (int y, int x) moveDir)
{
var xPos = curNode.x + moveDir.x;
var yPos = curNode.y + moveDir.y;
if (xPos < 0 || xPos >= tile.GetLength(1) || yPos < 0 || yPos >= tile.GetLength(0))
return true;
return tile[yPos, curNode.x].Weight == 0 &&
tile[curNode.y, xPos].Weight == 0;
}
}[경로 복원과 대각선 이동 검사 함수]
'Unity,C# > 알고리즘' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [정렬 알고리즘, C#] 버블 정렬(Bubble Sort) (1) | 2025.06.17 |
|---|---|
| [C#, Unity, 최단경로(PathFinding)] TileMap A* 알고리즘 (0) | 2025.04.10 |
| [C#, Algorithm] Dynamic Programming(동적 계획법) (0) | 2025.04.10 |
| [C#, Algorithm] 그라디(탐욕, 욕심쟁이) 알고리즘 (2) | 2025.04.10 |
| [C#, Unity, 최단경로(PathFinding)] TileMap 너비우선탐색(BFS) 알고리즘 (1) | 2025.04.07 |
